Residency Program - Case of the Month
March 2012 - Presented by Enko Kiprilov, M.D.
Answer:
Metastatic carcinoma consistent with lung primary
Discussion:
Cancer found outside of the lung may be determined to have arisen within the lung, as lung cancers that metastasize often retain a specific cell marker profile that allows determination of the lung as the primary site of origin. Primary lung cancers of adenocarcinoma histology typically have nuclear immunostaining with TTF-1 (1, 2).
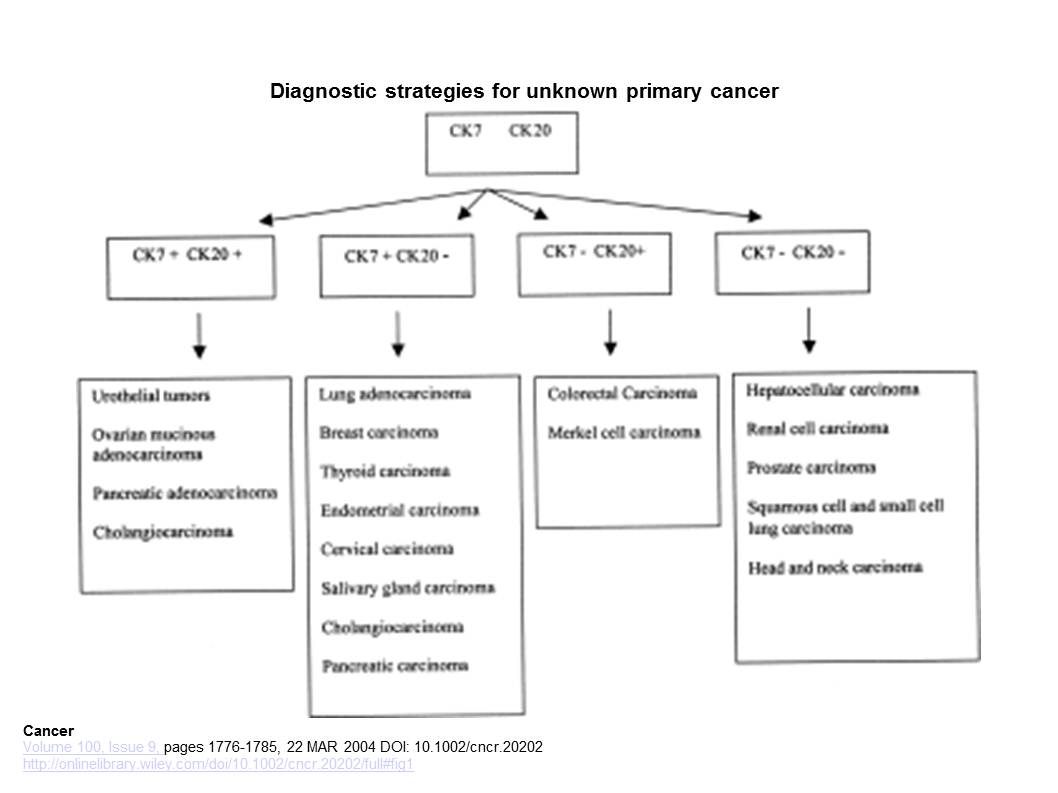
Additional Markers Used as Suggested by Clinical Data (after a Preliminary Workup with CK7 and CK20) Tumor Marker (3).
| Urothelial carcinoma | UROIII, THR, HMWCK |
| Breast carcinoma | GCDFP-15, ER, PR |
| Lung (mainly adenocarcinoma) | TTF-1, surfactant A and B |
| Medullary thyroid carcinoma | TTF-1, Calcitonin |
| Merkel cell carcinoma | CD117 |
| Hepatocellular carcinoma | Hep par-1 |
| Prostate carcinoma | PSA, PAP |
| Cholangiocarcinoma | CK19 |
| Mesothelioma | Calretinin |
UROIII: uroplakin III; THR: thrombomodulin; HMWCK: high molecular weight cytokeratin; GCDFP-15: gross cystic disease fluid protein-15; ER: estrogen receptor; PR: progesterone receptor; TTF-1: thyroid transcription factor-1; PSA: prostate-specific antigen; PAP: prostate acid phosphatase.
References:
- Tan D, Zander DS (2008). Immunohistochemistry for Assessment of Pulmonary and Pleural Neoplasms: A Review and Update. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 1 (1): 19–31. PMC 2480532. PMID 18784820.
- Park SY, Kim BH, Kim JH, Lee S, Kang GH (2007). Panels of immunohistochemical markers help determine primary sites of metastatic adenocarcinoma. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 131 (10).
- Varadhachary GR, Abbruzzese JL, Lenzi R (2004). Diagnostic strategies for unknown primary cancer. Cancer. 2004 May 1;100(9):1776-85.

 Meet our Residency Program Director
Meet our Residency Program Director
 LeShelle May
LeShelle May Chancellor Gary May
Chancellor Gary May